Lidar, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth.
ALS is a remote sensing technique used for mapping of topography, vegetation, urban areas, ice, and infrastructure. It is often referred to as light detection and ranging because it uses a laser to illuminate the Earth's surface and a photodiode to register the backscatter radiation. In addition to providing dense data across large open areas of open Terrain, Lidar is distinguished from other remote sensing technologies by its ability to provide data from terrain and objects under the forest canopy. As a Lidar sensor is flown over a forested, woodland, or scrub landscape area some returns will penetrate the vegetation canopy, reach the ground, and return to be recorded by the sensor- effectively allowing the creation of terrain models as ‘seen through trees. Producing Digital Terrain and surface models is considered the main application of ALS. It is mainly used in surveying, Archaeology, Urban planning, and environmental management and research like Forestry, Geology, Geomorphology and seismology
Accurate three dimensional 3D point cloud have been an important data source for 3D urban models, which are an integral part of urban planning, simulation ,mapping and visualization. MLS is an emerging technology for generating highly accurate 3D point clouds and thus have much potential mobile application. MLS is a land surveying method that uses laser system mounted on moving vehicles. MLS can be mounted on land based vehicles such as cars, trains and trucks .Airborne vehicle such as UAVs and helicopter or boats. This type of remote sensing surveys landscapes, cityscapes, buildings and infrastructure corridors such as railways and roads. Usually the traditional surveying process takes lot of time, interrupts the day to day traffic activities and requires many on-site workers . Typically MLS systems are able to acquire three dimensional point clouds with 1-10 centimeter point spacing at a normal driving or walking speeding in the street or indoor environments. Mobile laser scanners can reduces the time and money spent on these surveys, freeing up the project budget for other operations and processes. MLS comes in handy in emergency response situations to analyse ground condition quickly as well as for mapping projects like Street view and Google Maps
Terrestrial laser scanners are used for detailed 3D data acquisition of objects. Laser scanning is a very fast and cheap way to produce 3D models. TLS is a surveying technique performed using ground lasers. After processing each point is assigned with X,Y,Z coordinates, color and reflectance value . It also facilitates the assessment of the stability of earthworks. The most important advantage of the method is that very high point density can be achieved , in the order of 1 to 10 mm resolution. According to its scanning space, it is roughly divided into terrestrial laser scanner ,vehicle mounted scanner and handheld scanner. TLS have applications in many different areas such as deformation measurements ,quality control or topographical survey,cultural heritage monitoring , Mining, As built surveying ,Architecture, Archaeology ,Monitoring ,Civil Engineering and City Modeling
This project was aimed at Producing DSM output with total planimetric area of 600 Sq.km.
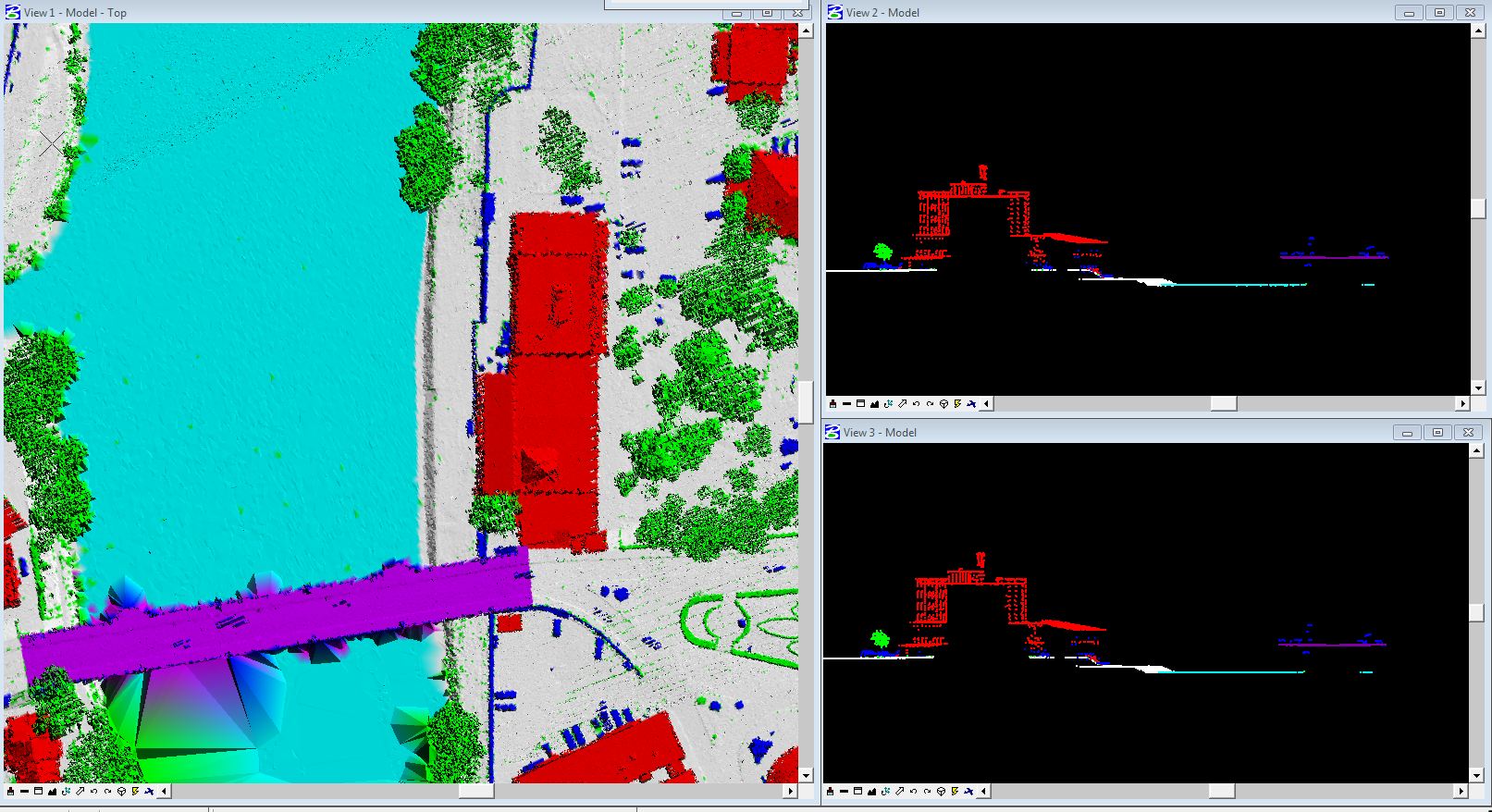
Point Cloud Classification is a task involving the classification of unordered 3D point sets.
Every lidar point can have a classification assigned to it that defines the type of object that
has reflected the laser pulse. Lidar points can be classified into a number of categories
including bare earth or ground, top of canopy, and water. The different classes
are defined using numeric integer codes in the LAS files.
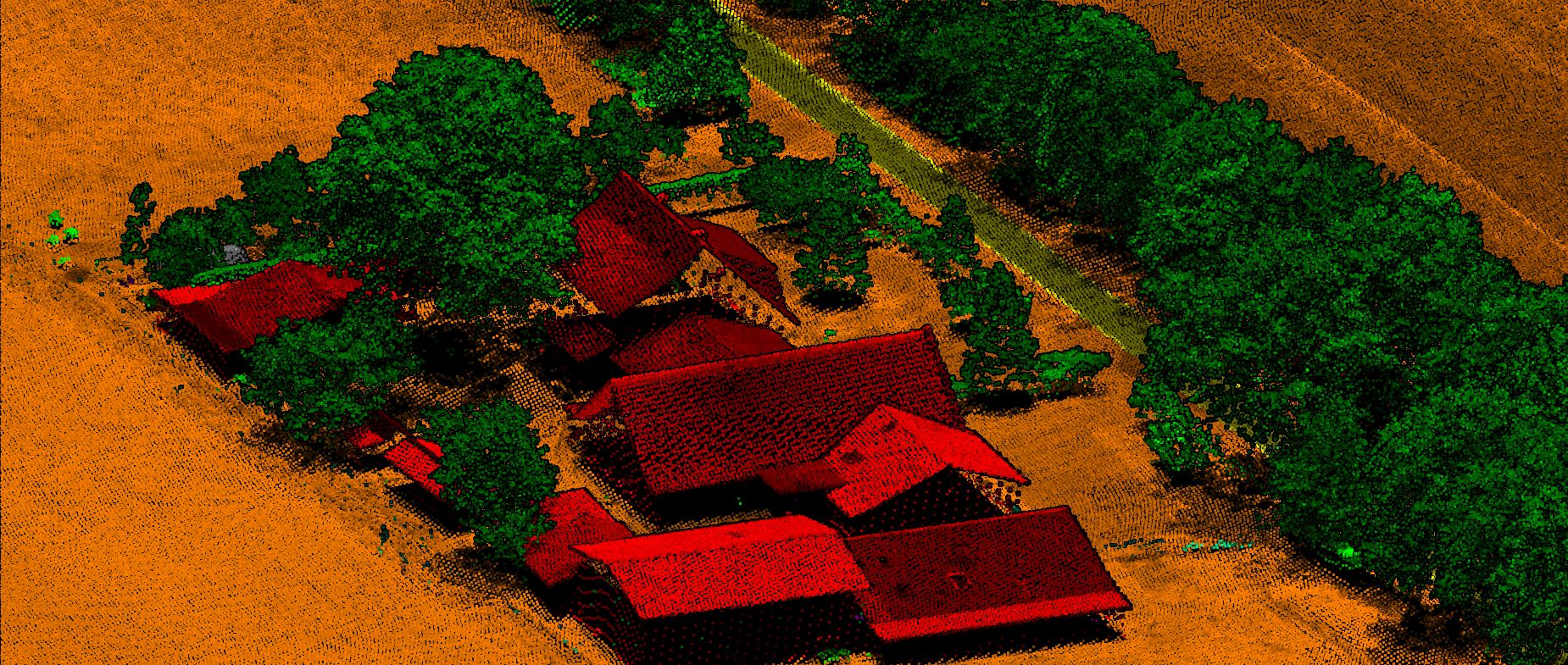
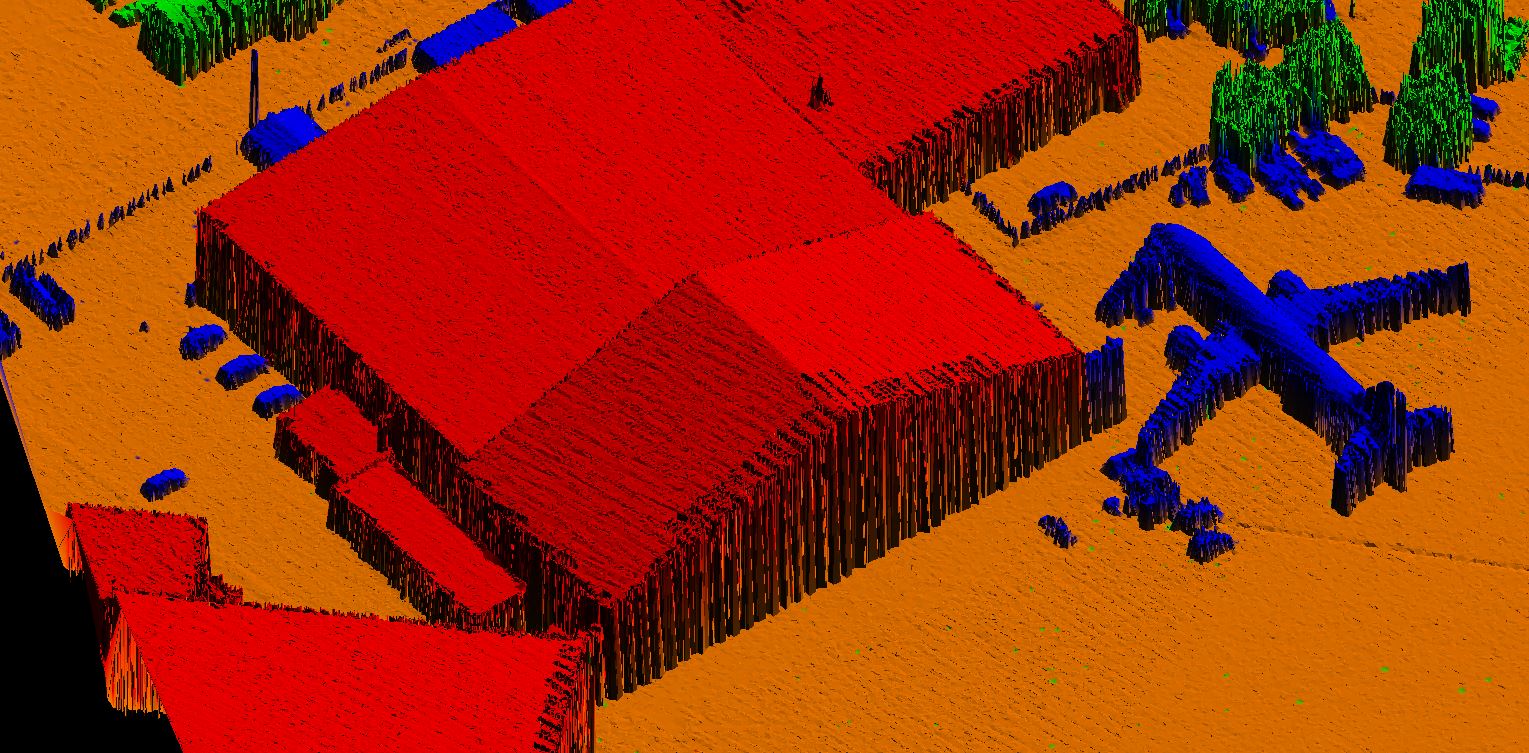
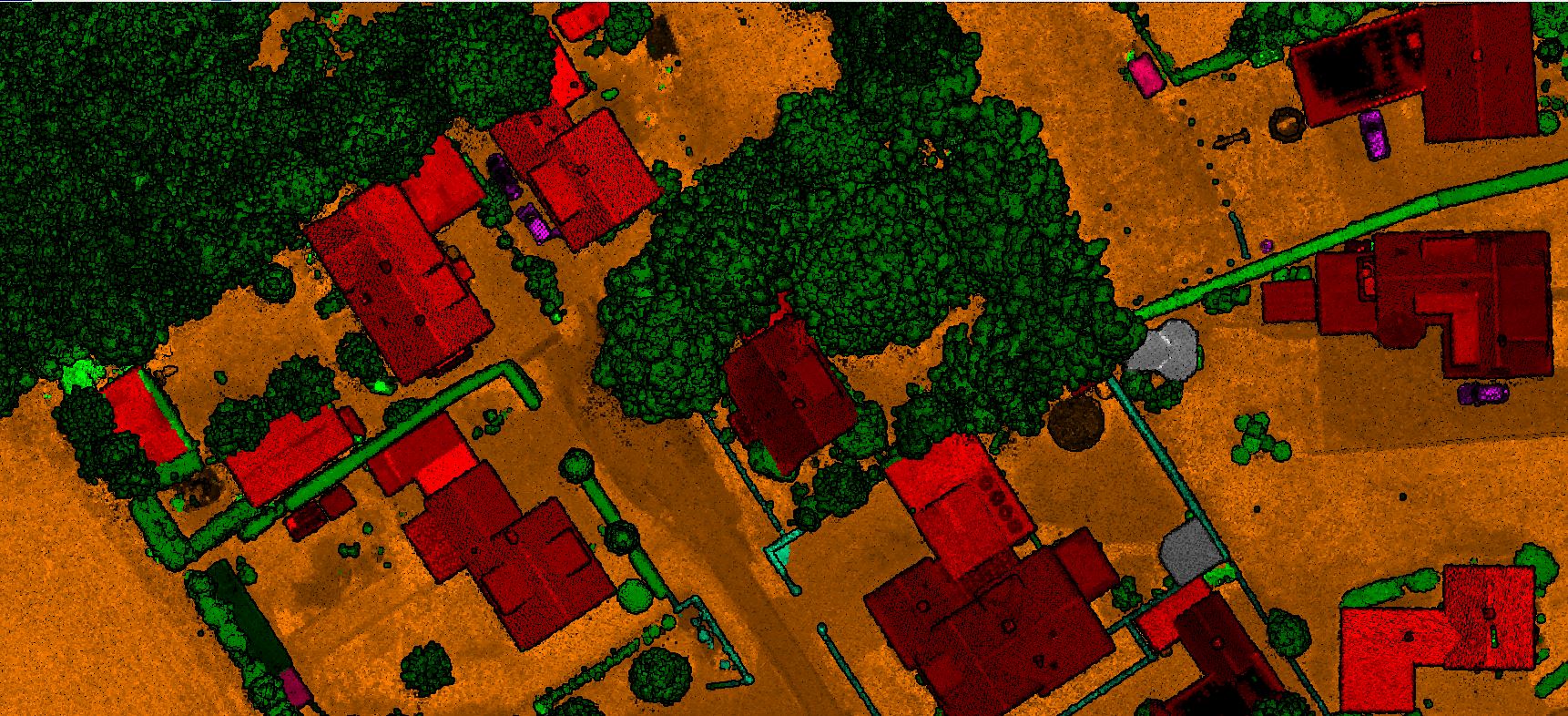

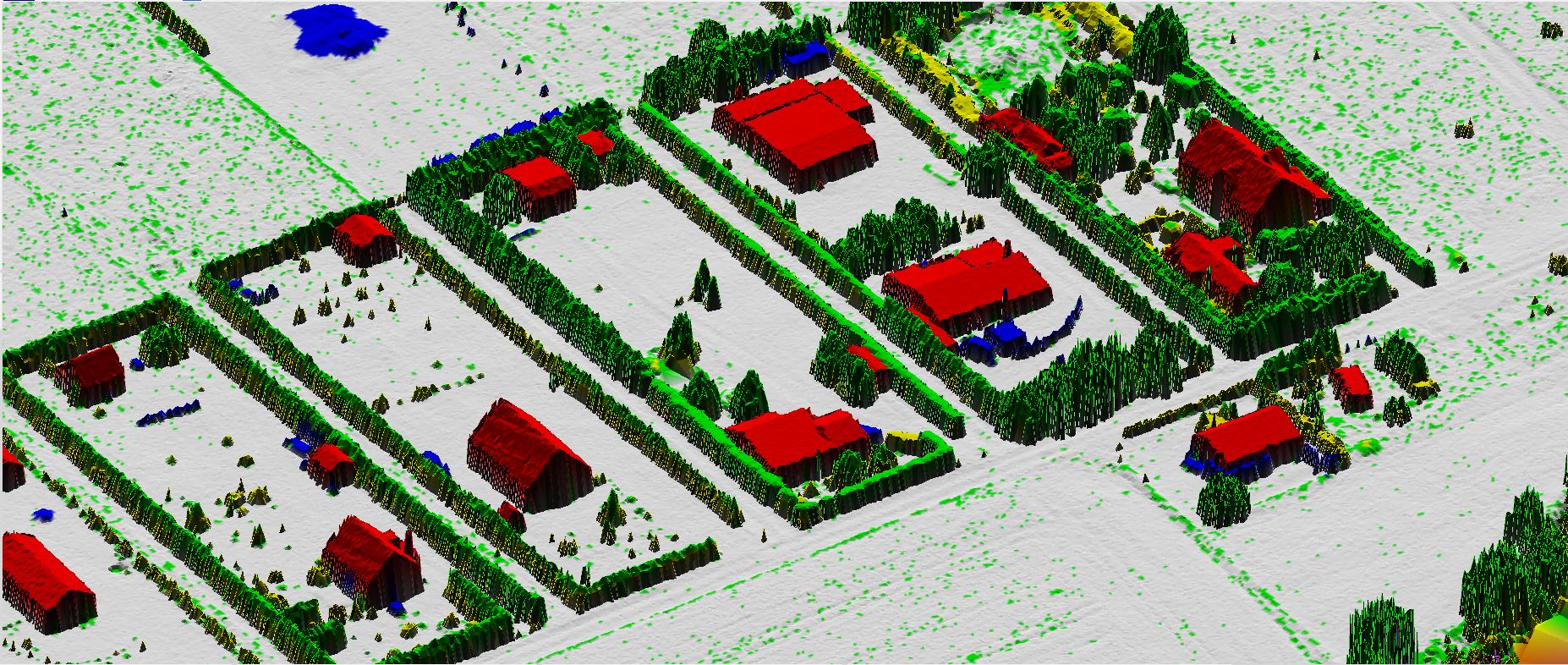
Digital Surface model is a topographic digital model which describes the relief and the situation on the surface. DSM represents the Mean sea level elevation of the reflective surface of Trees, Buildings and other features elevated above bare earth.
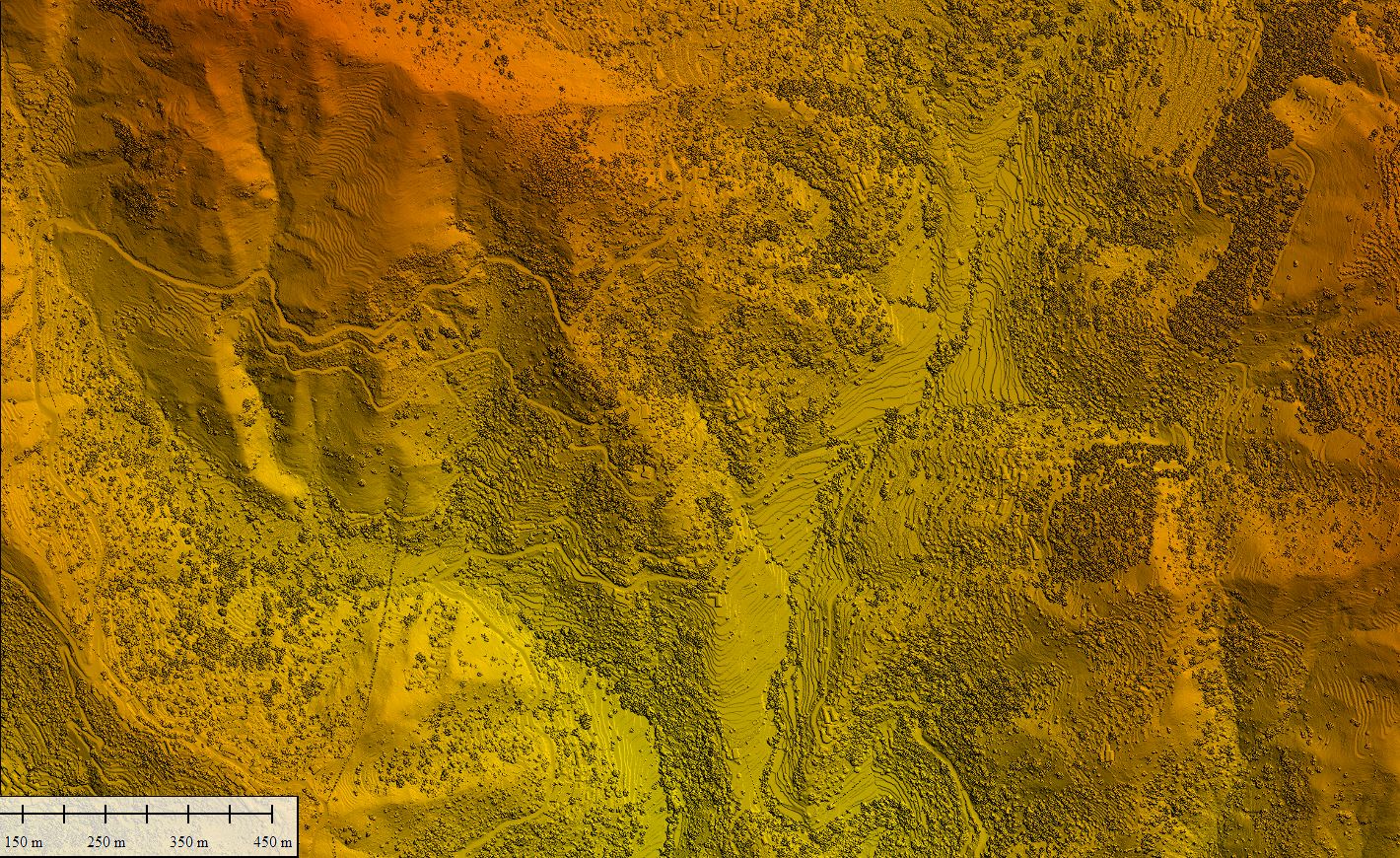
A digital elevation model is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain, commonly of a planet, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refers to a discrete global grid. DEMs are used often in geographic information systems, and are the most common basis for digitally produced relief maps
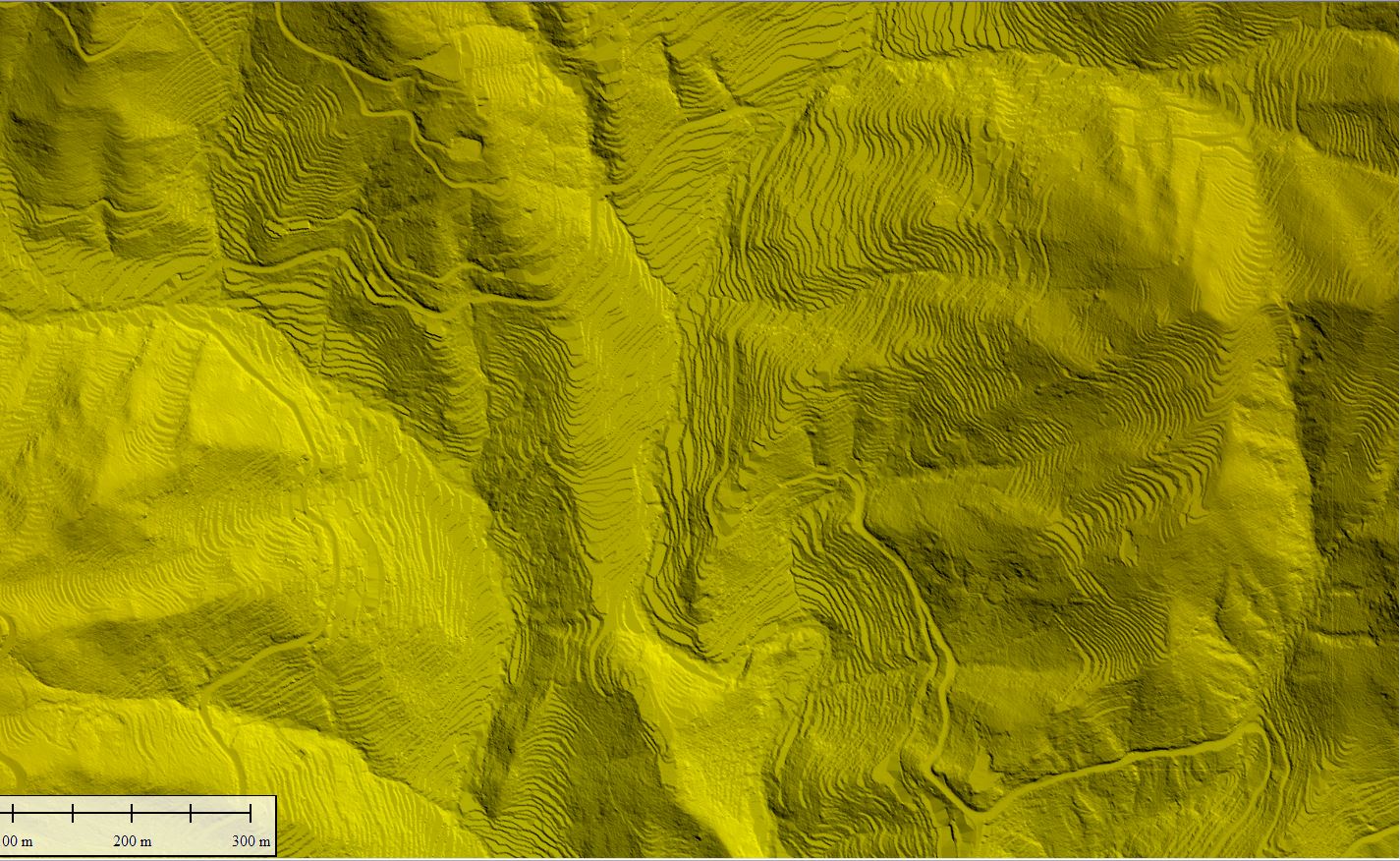

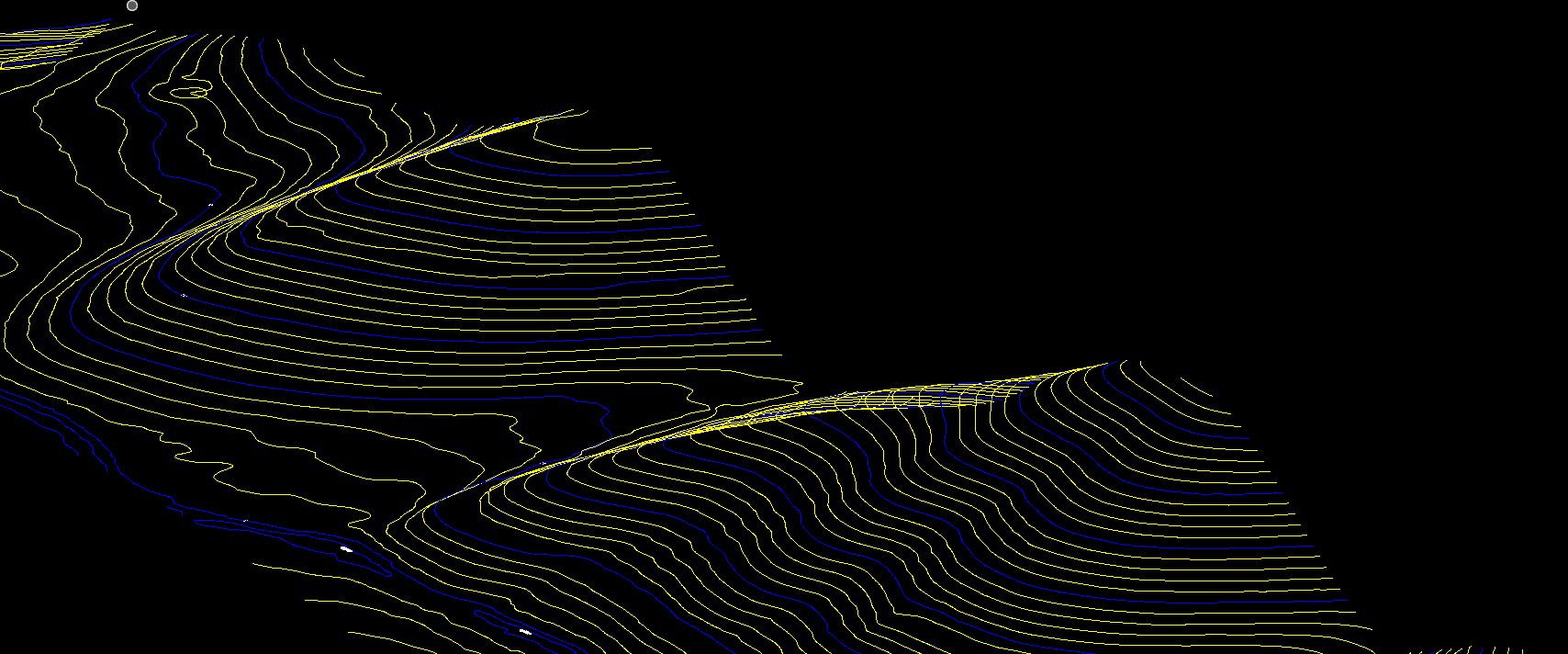
Contour represents points having equal heights /elevations concerning a particular datum such as Mean sea level (MSL).In the contour-based structure, the contour lines are traced from the topographic maps and are stored with their location(X, Y) and elevation information. Digital contours are used to generate polygons, and each polygon is tagged with the elevation information from the bounding contour.
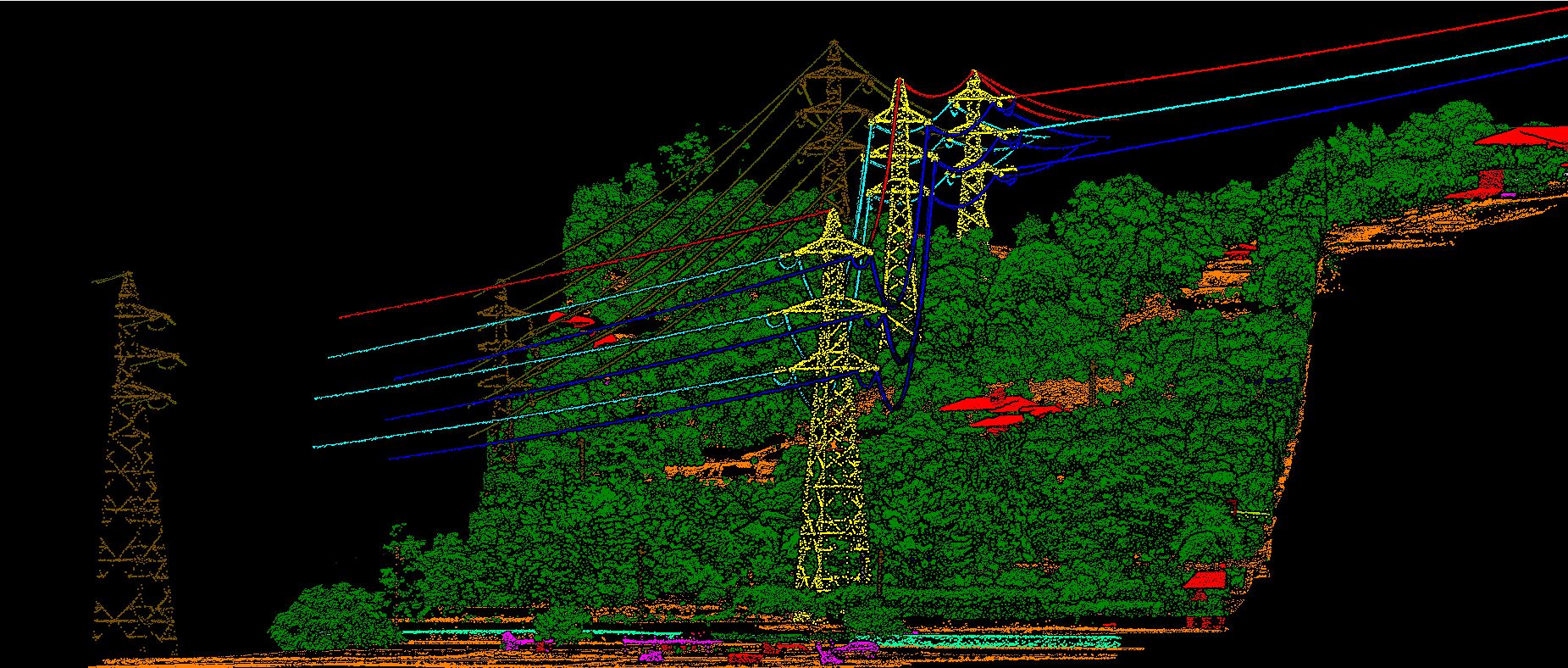
Power lines are extending to complex environments (e.g., lakes and forests), and the distribution of power lines in a tower is becoming complicated (e.g., multi-loop and multi-bundle). Additionally, power line inspection is becoming heavier and more difficult. LiDAR power line inspection enables grid operators to create 3D models which help to predict and detect future defects.

Hydrology is the study of the distribution and movement of water both on and below the Earth's surface, as well as the impact of human activity on water availability and conditions. GIS can be applied successfully to manage and monitor groundwater resources. It's possible to use GIS and remote sensing to identify water fluctuations and patterns, detect aquifer recharge zones, assess and classify periods of hydrological drought, identify vulnerable aquifers, and map areas with viable groundwater.
An UAV is a photogrammetrically orthorectified image product mosaicked from an image collection, where the geometric distortion has been corrected and the imagery has been color balanced to produce a seamless mosaic dataset